Understanding the **Risk of Ovarian Torsion After Hysterectomy**
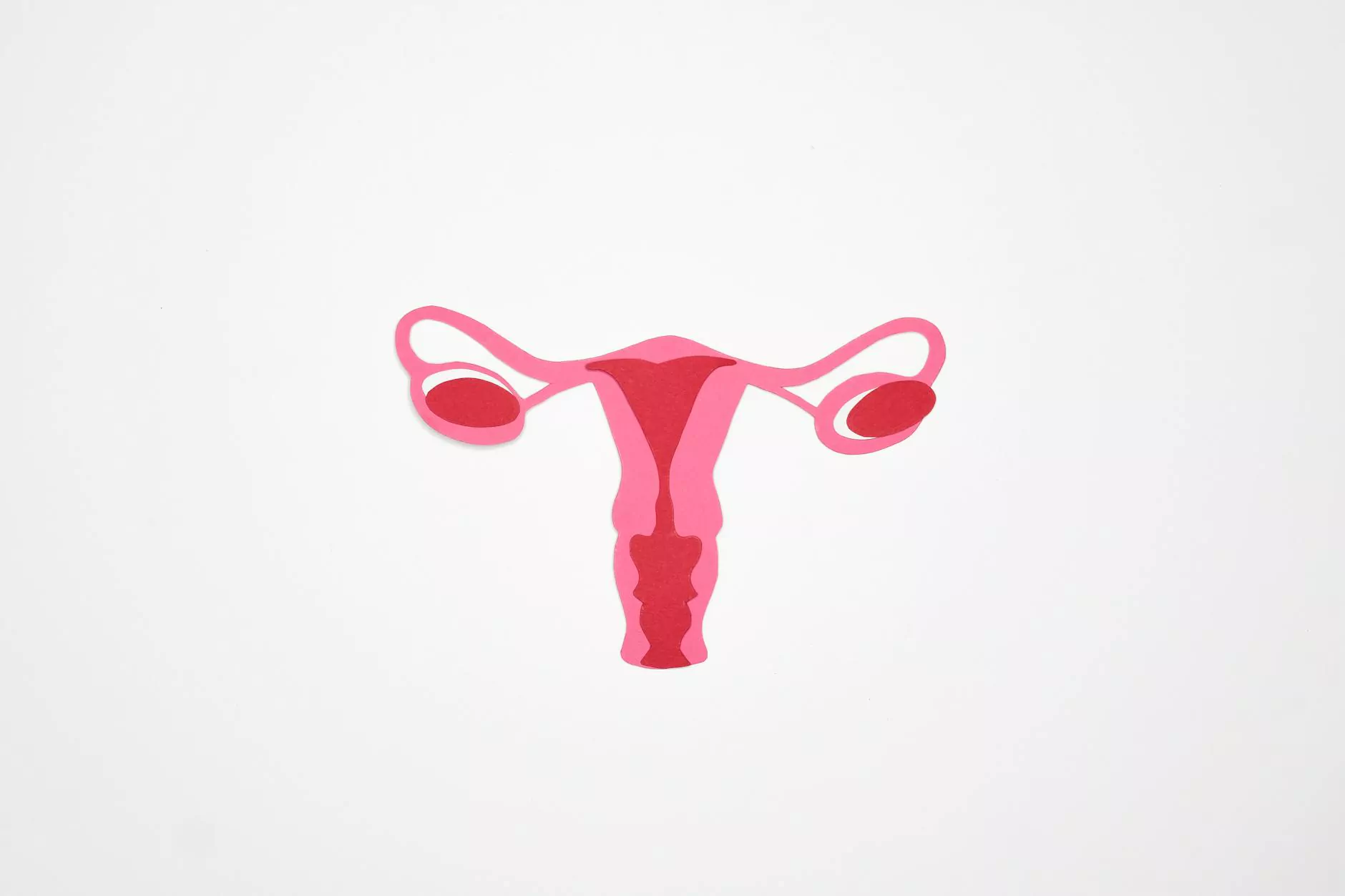

Hysterectomy, a surgical procedure to remove the uterus, is often performed for various medical reasons including fibroids, endometriosis, cancer, or chronic pain. While hysterectomy can offer relief and improve quality of life, it is not without risks and potential complications. One such complication that can arise in some cases is the risk of ovarian torsion after hysterectomy. This article aims to shed light on the intricacies of this condition, providing insight into symptoms, prevention strategies, and overall implications for women's health.
What is Ovarian Torsion?
Ovarian torsion occurs when an ovary becomes twisted, cutting off its blood supply. This condition may occur due to various factors, including anatomical predispositions, rapid weight changes, or even physical activity. Symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe abdominal pain. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent permanent damage to the ovary.
Why Consider the Risk of Ovarian Torsion After Hysterectomy?
While hysterectomy primarily focuses on the uterus, it may inadvertently affect the ovaries, especially if they are not removed during the procedure. For women who retain their ovaries post-hysterectomy, the risk of ovarian torsion can pose legitimate concerns. Recognizing this risk is essential for both healthcare providers and patients.
Factors Contributing to Ovarian Torsion After Hysterectomy
There are several factors that can contribute to the risk of ovarian torsion after hysterectomy:
- Anatomical Changes: The removal of the uterus may alter the structural makeup of the pelvic area, which can impact the stability of the ovaries.
- Scar Tissue: Surgery can lead to the formation of scar tissue that may adversely affect the blood supply to the ovaries.
- Hormonal Changes: Post-hysterectomy hormonal imbalances can lead to changes in the size and mobility of the ovaries.
- Activity Level: Increased physical activity or violent movements post-surgery can heighten the risk of twisting the ovary.
Symptoms of Ovarian Torsion
Identifying the signs and symptoms of ovarian torsion is critical for prompt intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Sudden, severe abdominal or pelvic pain: The pain may be localized or radiate to the lower back or thighs.
- Unexplained nausea and vomiting: These may accompany severe pain and indicate a need for immediate medical attention.
- Fever: Fever can be an indicator of infection, which may occur if the torsion leads to necrosis of the ovarian tissue.
- Changes in menstrual cycle: Women may experience unusual bleeding or changes in their cycle following a torsion episode.
Diagnosis of Ovarian Torsion
Diagnosis of ovarian torsion often involves the following steps:
- Physical Examination: Doctors will assess the patient's symptoms and conduct an abdomen and pelvic exam.
- Ultrasound Imaging: An ultrasound, particularly a Doppler ultrasound, can help visualize blood flow to the ovaries and detect torsion.
- CT or MRI: These imaging tests may be used if the diagnosis remains uncertain after initial evaluations.
Treatment Options for Ovarian Torsion
Immediate treatment is critical for ovarian torsion. Options may include:
- Emergency Surgery: In most cases, surgical intervention is required to untwist the affected ovary and restore blood flow.
- Laparoscopy: This minimally invasive surgery is often preferred to treat torsion, allowing for quicker recovery with less post-operative pain.
- Oophorectomy: In cases where the ovary has undergone significant damage, it may need to be removed.
Preventive Measures for Reducing the Risk of Ovarian Torsion After Hysterectomy
While not all instances of ovarian torsion can be prevented, certain measures can help mitigate risks:
- Follow Post-operative Guidelines: Adhering to your doctor's advice on activity levels after surgery can be crucial.
- Regular Check-ups: Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider will ensure any complications are detected early.
- Stay Informed: Understanding the signs and symptoms of ovarian torsion allows for quicker response times if issues arise.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in moderate physical activity can support overall reproductive health.
Living with Awareness: The Importance of Education
Education and awareness are key components in managing women’s health after a hysterectomy. Understanding the risk of ovarian torsion after hysterectomy empowers women to seek medical help promptly when symptoms arise. Make it a point to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider who can offer personalized advice.
Conclusion
In summary, while the risk of ovarian torsion after hysterectomy is a legitimate concern for women who retain their ovaries, heightened awareness and early intervention can make all the difference in treatment outcomes. By recognizing the symptoms, understanding the factors that contribute to torsion, and following preventative measures, women can significantly reduce their risk. Remember, your health is your most valuable asset—take care of it, and don't hesitate to seek help when necessary.
For more information, resources, and support regarding post-hysterectomy health, visit drseckin.com. Your health journey is important, and we are here to help.